雪花算法
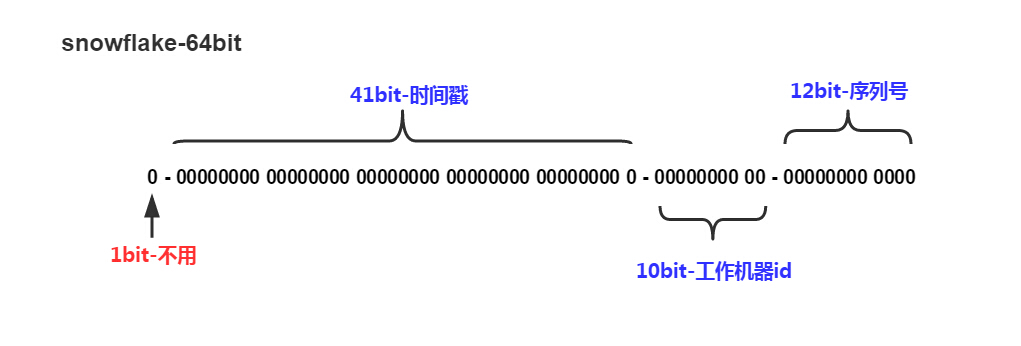
雪花算法简单描述:
- 最高位是符号位,始终为0,不可用。
- 41位的时间序列,精确到毫秒级,41位的长度可以使用69年。时间位还有一个很重要的作用是可以根据时间进行排序。
- 10位的机器标识,10位的长度最多支持部署1024个节点。
- 12位的计数序列号,序列号即一系列的自增id,可以支持同一节点同一毫秒生成多个ID序号,12位的计数序列号支持每个节点每毫秒产生4096个ID序号。
看的出来,这个算法很简洁也很简单,但依旧是一个很好的ID生成策略。其中,10位器标识符一般是5位IDC+5位machine编号,唯一确定一台机器。
<?php
namespace app\helpers;
/**
* 雪花算法类
* @package app\helpers
*/
class SnowFlake
{
const EPOCH_OFFSET = 0; //偏移时间戳,该时间一定要小于第一个id生成的时间,且尽量大(影响算法的有效可用时间)
const SIGN_BITS = 1; //最高位(符号位)位数,始终为0,不可用
const TIMESTAMP_BITS = 41; //时间戳位数(算法默认41位,可以使用69年)
const DATA_CENTER_BITS = 5; //IDC(数据中心)编号位数(算法默认5位,最多支持部署32个节点)
const MACHINE_ID_BITS = 5; //机器编号位数(算法默认5位,最多支持部署32个节点)
const SEQUENCE_BITS = 12; //计数序列号位数,即一系列的自增id,可以支持同一节点同一毫秒生成多个ID序号(算法默认12位,支持每个节点每毫秒产生4096个ID序号)。
/**
* @var integer 数据中心编号
*/
protected $data_center_id;
/**
* @var integer 机器编号
*/
protected $machine_id;
/**
* @var null|integer 上一次生成id使用的时间戳(毫秒级别)
*/
protected $lastTimestamp = null;
/**
* @var int
*/
protected $sequence = 1; //序列号
protected $signLeftShift = self::TIMESTAMP_BITS + self::DATA_CENTER_BITS + self::MACHINE_ID_BITS + self::SEQUENCE_BITS; //符号位左位移位数
protected $timestampLeftShift = self::DATA_CENTER_BITS + self::MACHINE_ID_BITS + self::SEQUENCE_BITS; //时间戳左位移位数
protected $dataCenterLeftShift = self::MACHINE_ID_BITS + self::SEQUENCE_BITS; //IDC左位移位数
protected $machineLeftShift = self::SEQUENCE_BITS; //机器编号左位移位数
protected $maxSequenceId = -1 ^ (-1 << self::SEQUENCE_BITS); //最大序列号
protected $maxMachineId = -1 ^ (-1 << self::MACHINE_ID_BITS); //最大机器编号
protected $maxDataCenterId = -1 ^ (-1 << self::DATA_CENTER_BITS); //最大数据中心编号
/**
* @param integer $dataCenter_id 数据中心的唯一ID(如果使用多个数据中心,需要设置此ID用以区分)
* @param integer $machine_id 机器的唯一ID (如果使用多台机器,需要设置此ID用以区分)
* @throws \Exception
*/
public function __construct($dataCenter_id = 0, $machine_id = 0)
{
if ($dataCenter_id > $this->maxDataCenterId) {
throw new \Exception('数据中心编号取值范围为:0-' . $this->maxDataCenterId);
}
if ($machine_id > $this->maxMachineId) {
throw new \Exception('机器编号编号取值范围为:0-' . $this->maxMachineId);
}
$this->data_center_id = $dataCenter_id;
$this->machine_id = $machine_id;
}
/**
* 使用雪花算法生成一个唯一ID
* @return string 生成的ID
* @throws \Exception
*/
public function generateID()
{
$sign = 0; //符号位,值始终为0
$timestamp = $this->getUnixTimestamp();
if ($timestamp < $this->lastTimestamp) {
throw new \Exception('时间倒退了!');
}
//与上次时间戳相等,需要生成序列号.不相等则重置序列号
if ($timestamp == $this->lastTimestamp) {
$sequence = ++$this->sequence;
if ($sequence == $this->maxSequenceId) { //如果序列号超限,则需要重新获取时间
$timestamp = $this->getUnixTimestamp();
while ($timestamp <= $this->lastTimestamp) { //时间相同则阻塞
$timestamp = $this->getUnixTimestamp();
}
$this->sequence = 0;
$sequence = ++$this->sequence;
}
} else {
$this->sequence = 0;
$sequence = ++$this->sequence;
}
$this->lastTimestamp = $timestamp;
$time = (int)($timestamp - self::EPOCH_OFFSET);
$id = ($sign << $this->signLeftShift) | ($time << $this->timestampLeftShift) | ($this->data_center_id << $this->dataCenterLeftShift) | ($this->machine_id << $this->machineLeftShift) | $sequence;
return (string)$id;
}
/**
* 获取去当前时间戳
*
* @return integer 毫秒级别的时间戳
*/
private function getUnixTimestamp()
{
return floor(microtime(true) * 1000);
}
}
本文收藏来自互联网,仅用于学习研究,著作权归原作者所有,如有侵权请联系删除
markdown 9ong@TsingChan
部分引用格式为收藏注解,比如本句就是注解,非作者原文。
